Kazakhstani reference genome database is being created at NU
Scientists from the National Laboratory Astana (NLA) are conducting large-scale studies of the Kazakhstani population’s entire genome using various sequencing technologies and bioinformatics analysis based on artificial intelligence (AI).
“The project will create a genome reference database of Kazakhstanis by sequencing the whole genomes of 500 individuals. Representatives from all major ethnic groups in Kazakhstan will be in the database, and AI technologies will be used in this work. The methodology of this project is unique in that it will use both the next generation sequencing (NGS) and third generation sequencing (TGS) technologies,” said Dr. Ainur Akilzhanova, Head of the Laboratory of Genomic and Personalized Medicine, Center of Life Sciences, NLA.
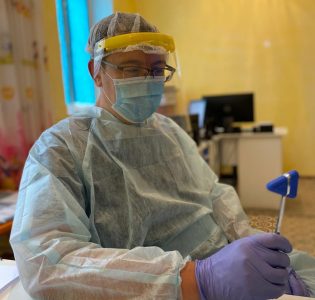
During the first period of this large-scale project, researchers visited rural areas and regions of the Republic. In November 2019, they visited Zhansary, a village in the Karaganda region. In August of this year, they toured a few villages of the Zhangeldy district in the Kostanay region. Scientists actively worked with patients in the village hospitals to register participants, take surveys, consult on the project, and gather biomaterials. All patients who participated had a chance to consult with doctors about their medical condition and have any questions answered.
Since the pandemic began, special attention has been paid to safety. In the villages that were visited, medical procedures were carried out in compliance with epidemiological norms and rules for distancing in the pandemic. Antiseptics and hand sanitizers were always used, personal protective equipment (e.g., disposable gloves, disposable medical underwear, surgical masks, shoe covers, etc.) were regularly replaced, workplace surfaces, protective face shields for personal protection and working tools were treated with antiseptic solutions.
During the second period of the research, all gathered biomaterials and data obtained will be analyzed and processed using high-performance genomic platforms (NGS, TGS) and modern bioinformatics methods.
According to Dr. Akilzhanova, using high-performance genomic platforms to study Kazakhstani genomes allows for greater understanding and development in the fields of health and biomedicine. The use of these data can help scientists and doctors assess the risk of various diseases and conditions, and really enhance of the development of digital medicine.
In addition, thanks to the study, scientists will be able to carry out a comparative analysis of genomes with those in the international databases of genomic variants, in order to determine the “place” of Kazakhstan’s population on the global map of human genomic variation.
A year ago researchers of the Laboratory of Bioinformatics and Systems Biology launched the first high-performance bioinformatics computational platform in Kazakhstan for dealing with the complexity of “big genomic data” and solving problems in the field of bioinformatics. The methodology developed for genomic analysis – BIODICA – is compatible with already existing bioinformatics computational platforms, and can even be used on a regular personal computer.
Read more:
NU launched a new computational system for genomic research and bioinformatics tasks solving